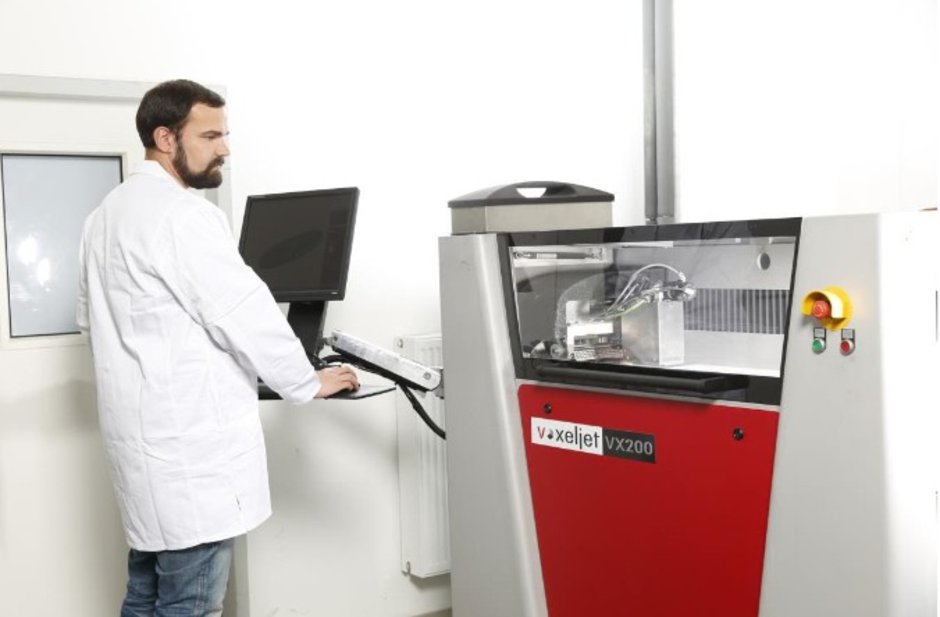
3D sand printing itself is not a novelty for foundries; though for a long time it has only been used for the production of prototypes and small series. Dr. Jens Muller, Global Head of R&D and Innovation at ASK Chemicals explains, “Withthe development of ever faster printers, especially in recent years, 3D sand printing offers foundries completely new possibilities and opportunities.Of course, binder technology has to be developed further, especially for these new productive systems. Iam therefore very pleased that we will be able to present new solutions for both inorganic and organic sand core production at GIFA 2019.”
A new requirement profileWith 3D sand printing using the powder binder jetting process, production of sand cores using contour-forming models and core tools is eliminated. The geometry of the sand cores is initially developed digitally based on CAD models. Next, the recoater applies a layer of a few hundred micrometers of quartz sand fully automatically. Then the binder liquid is selectively applied to the sand bed via the print head. The process of layered sand application by means of the recoater and selective binder input via the print head is repeated according to the specifications of the digital CAD model. Finally, the binder-free support sand is removed, and the printed component may betaken to a post-curing process.
The compatibility and durability of the print head components along with the chemical components of the binder fluid areas critical to achieving success as the application and dripping behavior of the fluid. This is collectively referred to as “print head compatibility”. The physical and chemical properties of the binder fluid play a crucial role in this process. The physical effects during selective binder input onto the sand bed, such as the migration of the fluid into the unprinted areas of the support sand, must be understood and controlled in order to ensure a high dimensional stability and low finishing cost of the sand cores produced. “Of course, 3D binders still also have to meet high thermal stability requirements to withstand the stresses during the casting process,” explains Dr. Müller.
New solutions for new requirementsThe development of NOVASET 3D, a phenolic resin binder for cold curing, has reduced the laborintensive finishing effort and drastically improved the process efficiency over standard binders. NOVASET 3D has a low veining tendency and guarantees clean casting surfaces for all types of casting.
The inorganic two-component system INOTEC 3D, consisting of an INOTEC 3D printing fluid and an INOTEC 3D promoter, is applicable for hot-curing additive manufacturing processes. “As a productive inorganic binder system, INOTEC 3D standsfor zero emissions during core productionand core storage and when using the sand cores in the casting process”, emphasizes Dr. Christian Appelt, Global Business Manager Inorganic Binder Systems at ASK Chemicals. Further advantages are the low finishing effort of the sand cores produced, which lead to castings of high dimensional accuracy and surface quality due to the high thermal stability. Above all, INOTEC 3D supports current trends in the engine casting segment of the light metal casting industry.
A special highlight at this year's booth will be the live demonstration of the inorganic binder INOTEC 3D inorganic binder on the new voxeljet VX1000-S printer.
Source: ASK
Partner
Foundry Daily News
GIFA 2019
GER - GIFA 2019: ASK Chemicals presents its binder technologies for additive manufacturing processes
Reading time: min
[0]